The Sense Organs
Key Notes :
Introduction to Sense Organs:
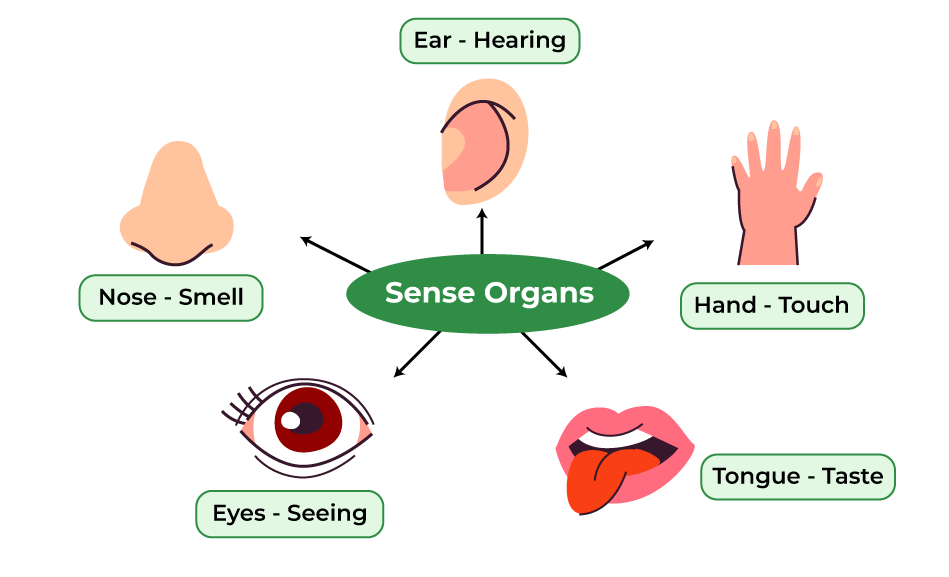
- Humans have five sense organs that help us understand the world around us.
- The five sense organs are: eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin.
The Eyes:
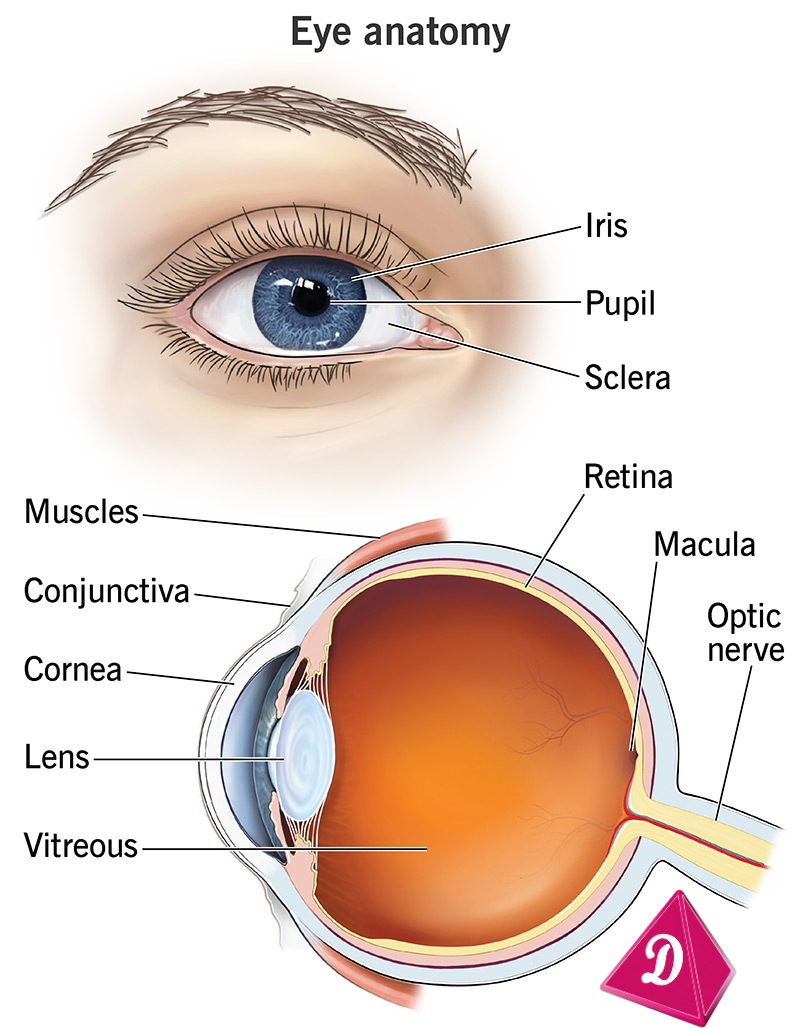
- Function: The eyes help us see.
- Parts: The parts of the eye include the cornea, lens, and retina.
- How it works: Light enters through the eye, and the brain helps us understand what we see.
The Ears:

- Function: The ears help us hear sounds.
- Parts: The parts of the ear include the outer ear, eardrum, and cochlea.
- How it works: Sound waves enter the ear, and signals are sent to the brain for interpretation.
The Nose:
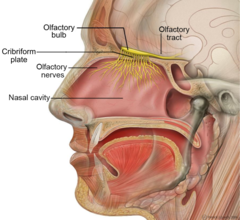
- Function: The nose helps us smell.
- Parts: The nose has nostrils, and inside are tiny cells that detect smells.
- How it works: Air carrying smells enters the nose, and the brain interprets the scent.
The Tongue:
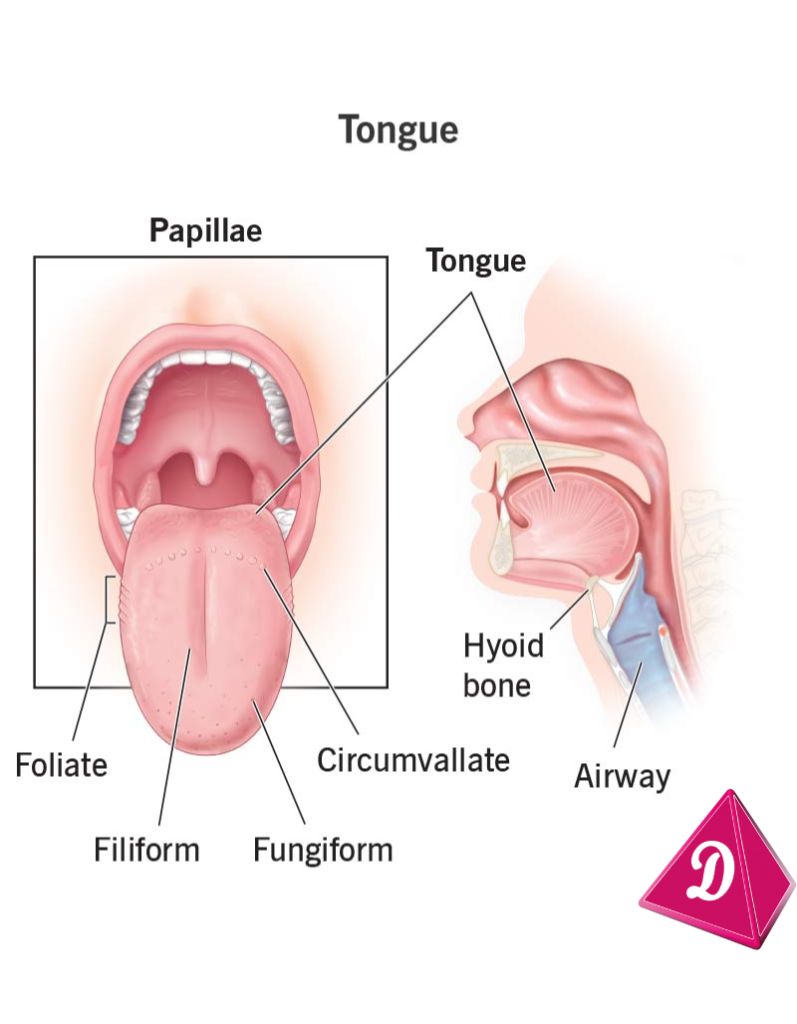
- Function: The tongue helps us taste.
- Parts: The tongue has taste buds that detect different flavors: sweet, salty, sour, and bitter.
- How it works: When we eat or drink, the tongue sends signals to the brain about the taste.
The Skin:
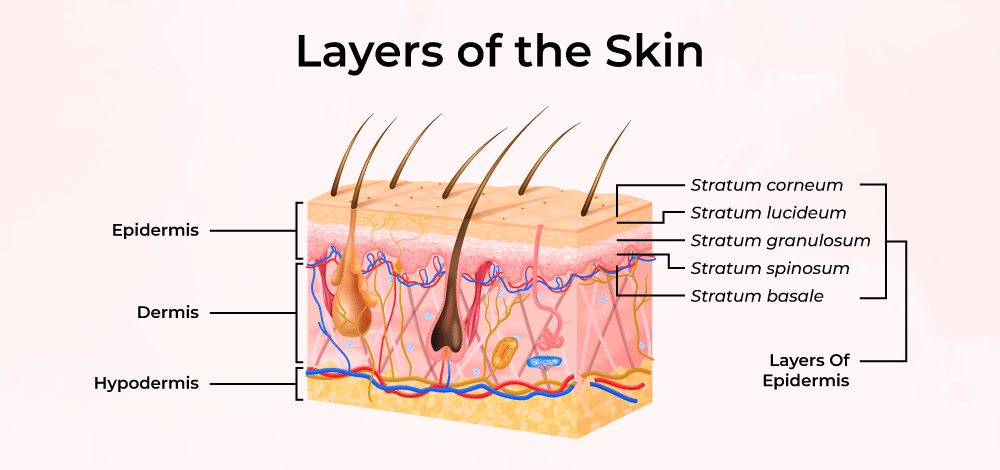
- Function: The skin helps us feel touch, heat, cold, and pain.
- Parts: The skin is the largest sense organ and has nerve endings that detect different sensations.
- How it works: When we touch something, the nerve endings in the skin send signals to the brain to tell us what we feel.
The Importance of Sense Organs:
- Sense organs are important because they help us interact with the world safely and understand our surroundings.
- They work together to help us learn about the environment, such as recognizing food, avoiding dangers, and enjoying nature.
Fun Facts:
- Did you know? Some animals have more developed senses than humans, such as dogs having a much better sense of smell.
- Our senses can help us enjoy activities like listening to music, tasting food, or feeling a soft blanket.
Let’s practice!

