What Are Birds
Key Notes :
Definition of Birds:

Birds are warm-blooded animals with feathers, wings, and beaks. They belong to a group of animals called Aves.
Physical Features:
- Feathers: All birds have feathers, which help them fly, stay warm, and attract mates.

- Wings: Birds have wings, although not all birds use them to fly (like ostriches and penguins).
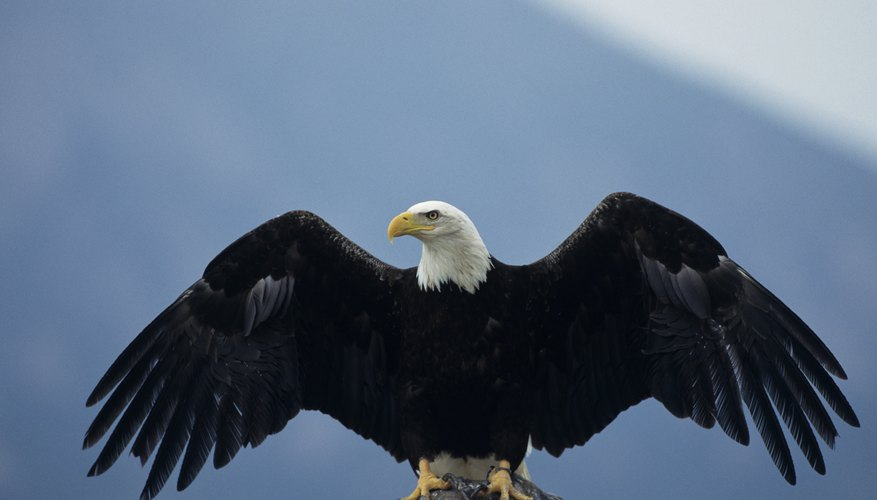

- Beaks: Birds have beaks instead of teeth, which they use to eat, groom, and build nests.

- Hollow Bones: Many birds have hollow bones, which make them light and help them fly.
Bird Habitats:
Birds live in various habitats, such as forests, deserts, wetlands, and cities. They adapt to their environment to find food, shelter, and nesting spots.
Types of Birds:
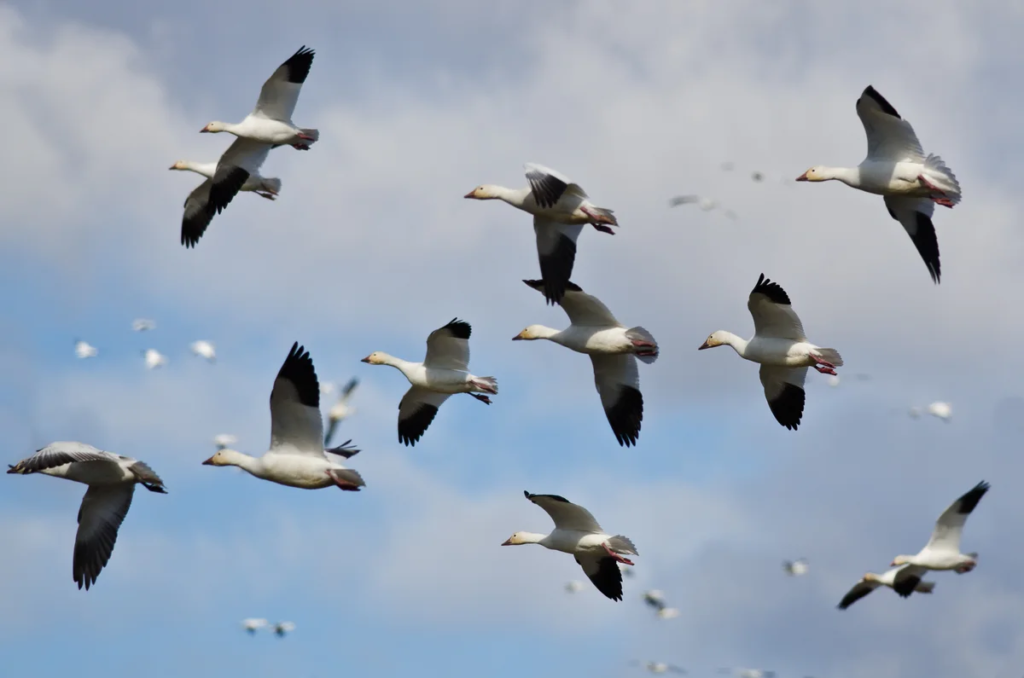
- Flying Birds: Examples include eagles, sparrows, and parrots.

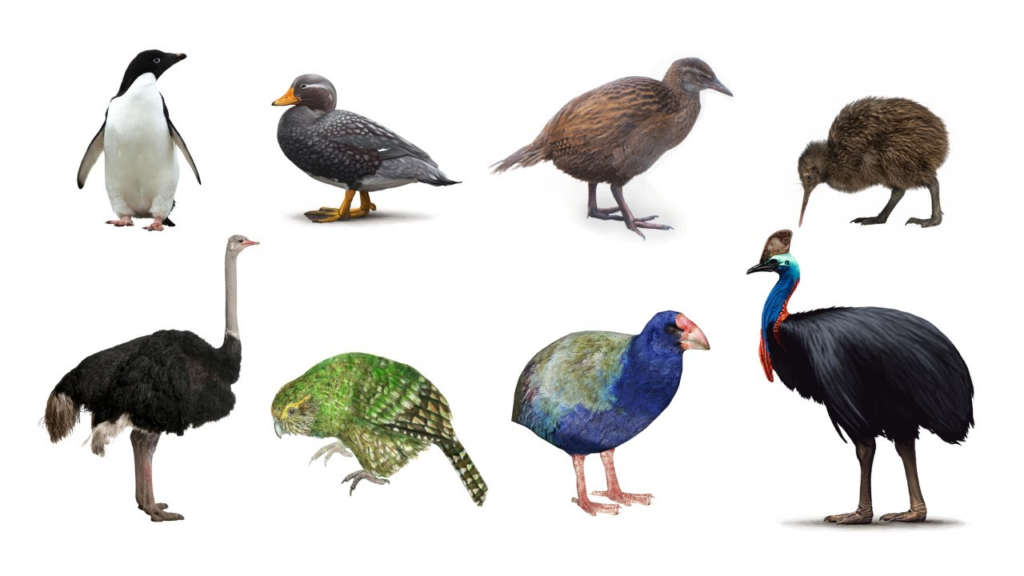
- Non-Flying Birds: Some birds, like ostriches, emus, and penguins, do not fly but have other adaptations like running or swimming.

Bird Diet:
- Birds eat different kinds of food, including insects, seeds, fruits, and small animals.
- Birds like hummingbirds sip nectar, while eagles eat meat.
Bird Nests:

Birds build nests to lay eggs and raise their young. Nests vary in shape and materials depending on the bird species.
Bird Migration:

Some birds travel long distances (migrate) to find food or better weather during certain seasons.
Importance of Birds:
Birds help pollinate plants, spread seeds, and keep insect populations in check, making them important to ecosystems.
Let’s practice!

