Food Chain
Key Notes :
Definition of Food Chain:
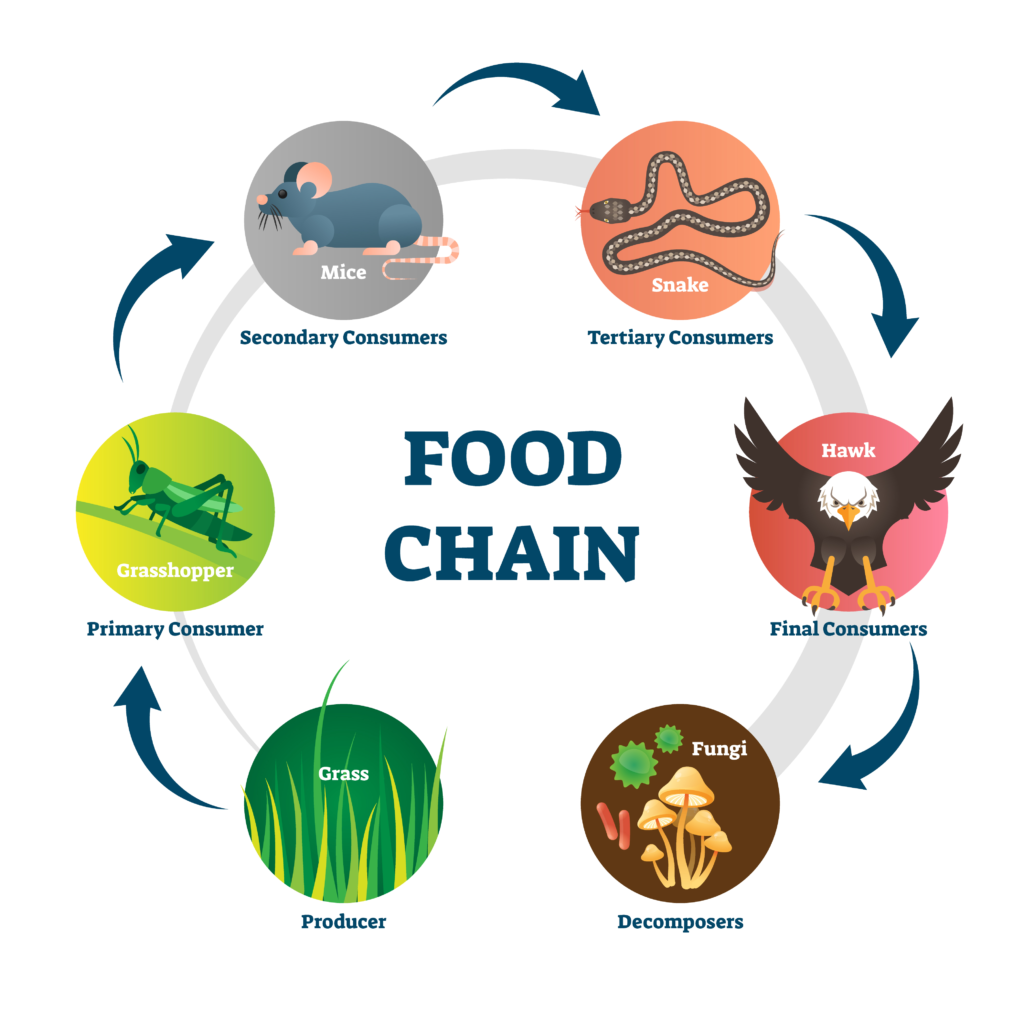
- A food chain shows how energy is passed from one living thing to another.
- It begins with plants and ends with animals.
Producers:
- Plants are called producers because they make their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide (photosynthesis).
Consumers:
Animals that eat plants or other animals are called consumers.
There are three types of consumers:
- Herbivores: Animals that eat only plants (e.g., deer, rabbits).

- Carnivores: Animals that eat other animals (e.g., lions, wolves).

- Omnivores: Animals that eat both plants and animals (e.g., humans, bears).

Decomposers:
- Decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down dead plants and animals, returning nutrients to the soil.
Energy Transfer:
- Energy flows from the sun to plants (producers) and then to animals (consumers).
- Each step in the food chain shows how energy is passed on.
Example of a Simple Food Chain:
- Sun → Grass (producer) → Grasshopper (herbivore) → Frog (carnivore) → Eagle (top carnivore).
Importance of Balance:
- All parts of the food chain depend on each other. If one part is removed, the balance is affected, which can harm the environment.
Food Web:
Multiple food chains in an ecosystem form a food web, showing how animals are connected through various food chains.
Let’s practice!

