Fishes
Key Notes :
What Are Fishes?
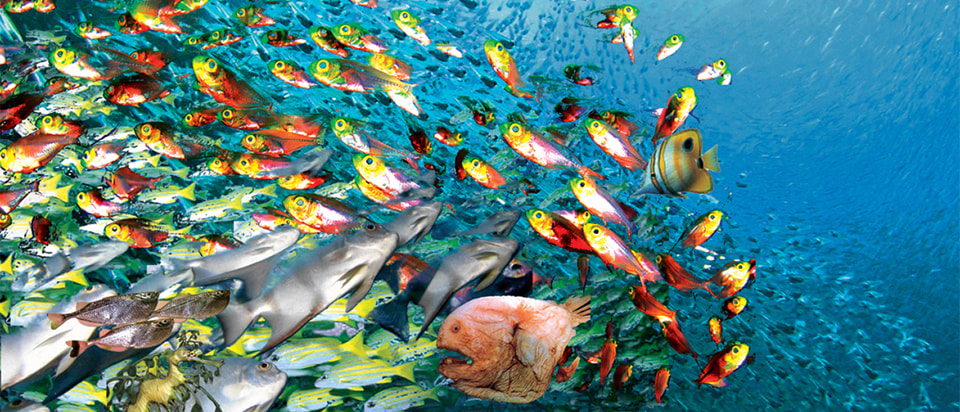

- Fishes are aquatic animals that live in water.
- They have gills for breathing, fins for swimming, and scales covering their bodies.
Types of Fishes:
- Freshwater Fish: Live in rivers, lakes, and ponds (e.g., goldfish, catfish).

- Saltwater Fish: Live in oceans and seas (e.g., salmon, clownfish).

Body Parts of Fish:
- Fins: Help fish swim and maintain balance.
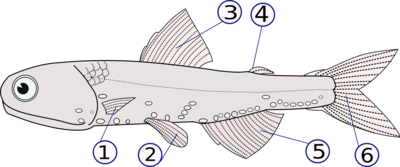
- Tail: Used for propulsion to move forward.

- Gills: Allow fish to breathe underwater by extracting oxygen from water.
- Scales: Protect their bodies and reduce water resistance.
Diet of Fishes:
- Fishes can be herbivores (plant eaters), carnivores (meat eaters), or omnivores (eat both plants and animals).
- Common foods include algae, small fish, and insects.
Habitat:
- Fishes live in various water environments, including oceans, rivers, lakes, and ponds.
- Some fishes prefer warm waters, while others thrive in colder environments.
Reproduction:
- Most fishes lay eggs in water, while some give birth to live young.
- Fish eggs are called roe, and many eggs hatch into fry (young fish).
Importance of Fishes:
- Fishes are a crucial part of the food chain in aquatic ecosystems.
- They provide food for humans and other animals.
- Fishes also contribute to recreational activities, like fishing and aquariums.
Conservation:
- Some fish species are endangered due to overfishing, pollution, and habitat loss.
- It is important to protect aquatic environments to ensure the survival of fish species.
Fun Facts:
- Some fish can change color to blend in with their surroundings.
- The largest fish in the world is the whale shark, which can grow up to 40 feet long!
Let’s practice!

