The Root

Key Notes :
Definition of a Root:
- The root is the part of a plant that grows underground and holds the plant in place.
- It absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.
Functions of Roots:
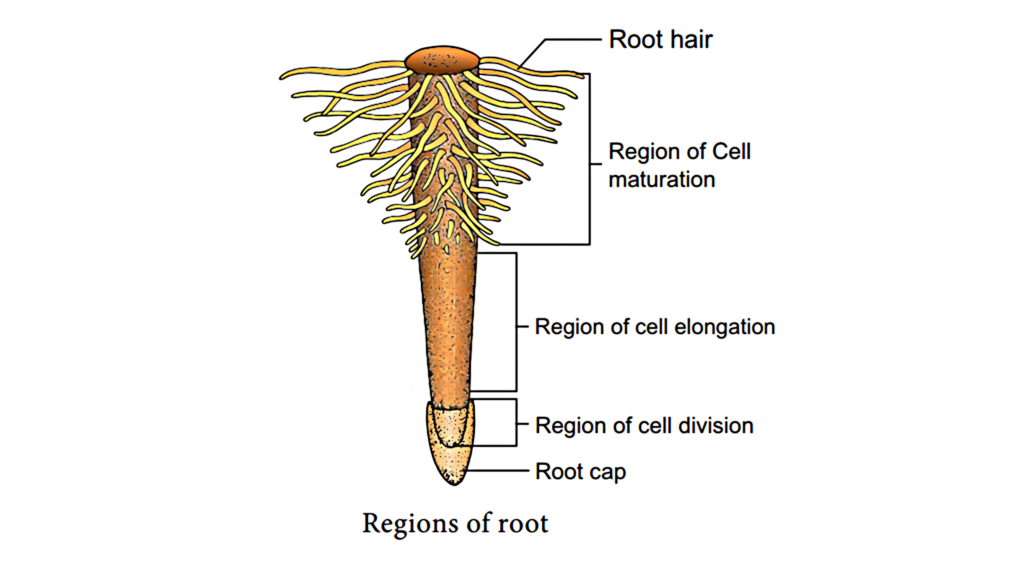
- Anchorage: Roots anchor the plant firmly in the ground.
- Absorption: Roots take in water and minerals needed for the plant to grow.
- Storage: Some roots store food for the plant (e.g., carrots, beets, radishes).
Types of Roots:
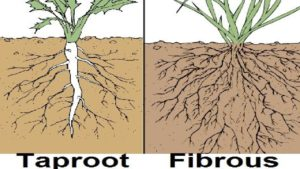
- Taproots: A single, thick main root with smaller side roots (e.g., carrot, radish).
- Fibrous Roots: A network of thin roots spreading out from the base of the stem (e.g., grass, wheat).
Structure of a Root:
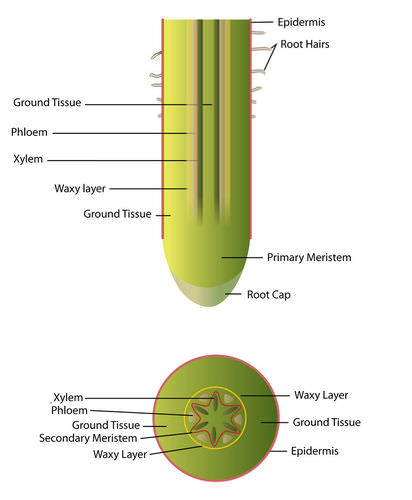
- Root Cap: Protects the tip of the root as it grows.
- Root Hairs: Tiny hair-like structures that increase the surface area for absorption.
Importance of Roots:
- Provide stability to the plant.
- Help plants get water and nutrients from the soil.
- Store food for human and animal consumption.
Examples of Roots We Eat:

- Carrots, beets, turnips, radishes, and sweet potatoes.
Fun Facts:
- The roots of some trees can grow as deep as 20 feet or more to reach water!
- Some plants, like mangroves, have roots that grow above the ground to help them breathe in swampy areas.
Let’s practice!

