The Seasons
Key Notes:
Definition of Seasons:
- A season is a part of the year marked by specific weather patterns and daylight hours.
- There are four main seasons: Spring, Summer, Autumn (Fall), and Winter.
Why Seasons Change:
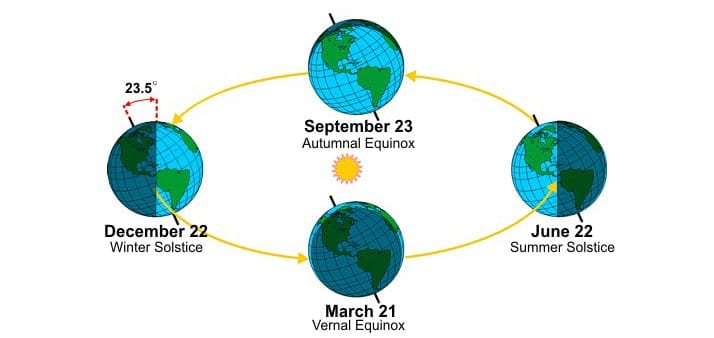
- Seasons change because of the Earth’s tilt and its orbit around the Sun.
- Different parts of the Earth get varying amounts of sunlight during the year.
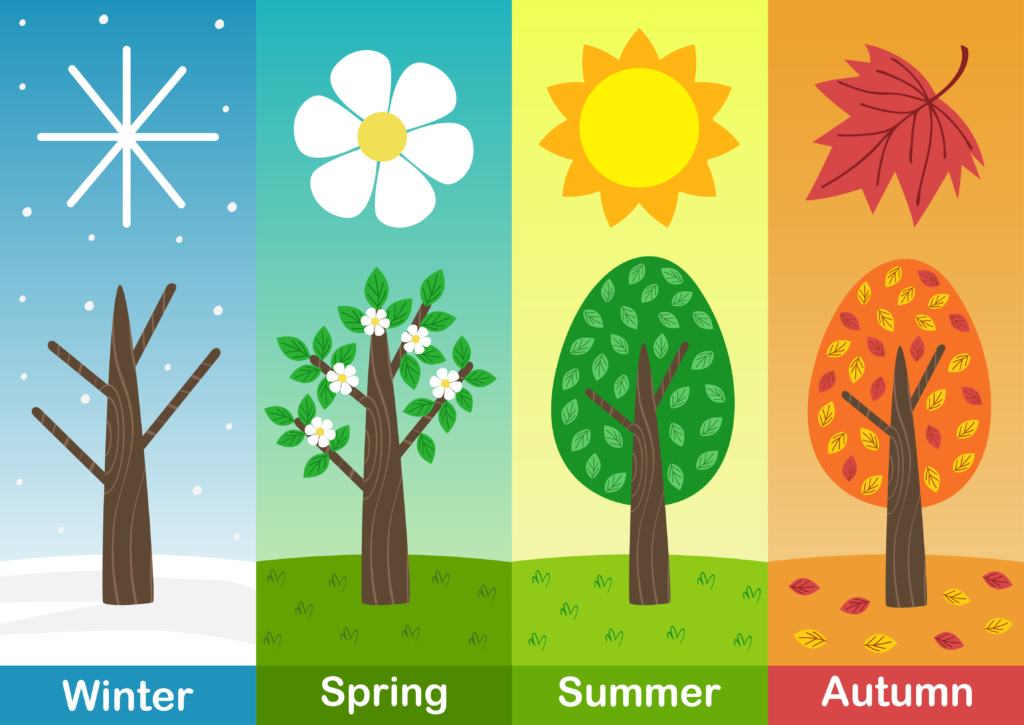
Characteristics of Each Season:
Spring:

- Weather is warmer, and plants start to grow.
- Flowers bloom, and animals become more active.
Summer:

- The hottest season with long days and short nights.
- Many people enjoy outdoor activities like swimming and picnics.
Autumn (Fall):

- Weather becomes cooler, and leaves change color and fall from trees.
- Farmers harvest crops.
Winter:

- The coldest season with short days and long nights.
- Snow may fall in some places, and animals hibernate.
Seasonal Activities:
- Spring: Planting gardens and celebrating new life.
- Summer: Going to the beach, eating ice cream, and wearing light clothes.
- Autumn: Raking leaves and enjoying pumpkin treats.
- Winter: Building snowmen, celebrating holidays, and wearing warm clothes.
Effects of Seasons on Living Things:
- Animals adapt by migrating, hibernating, or growing thick fur.
- Plants grow, shed leaves, or become dormant depending on the season.
Cultural Significance:
- Different cultures have special festivals or holidays related to seasons (e.g., Spring festivals, Harvest festivals, Winter holidays).
Interesting Facts:
- In some countries near the equator, there are only two main seasons: Rainy and Dry.
- Polar regions experience extreme seasons, with months of daylight in summer and darkness in winter.
Let’s practice!

