The Water Cycle
Key Notes:
What is the Water Cycle?
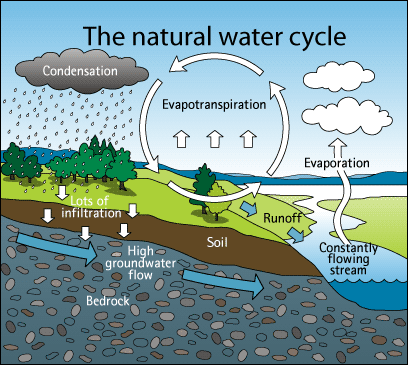
- The water cycle is the continuous movement of water on Earth through different forms (liquid, gas, and solid) and places (oceans, rivers, air, and land).
Main Processes of the Water Cycle:
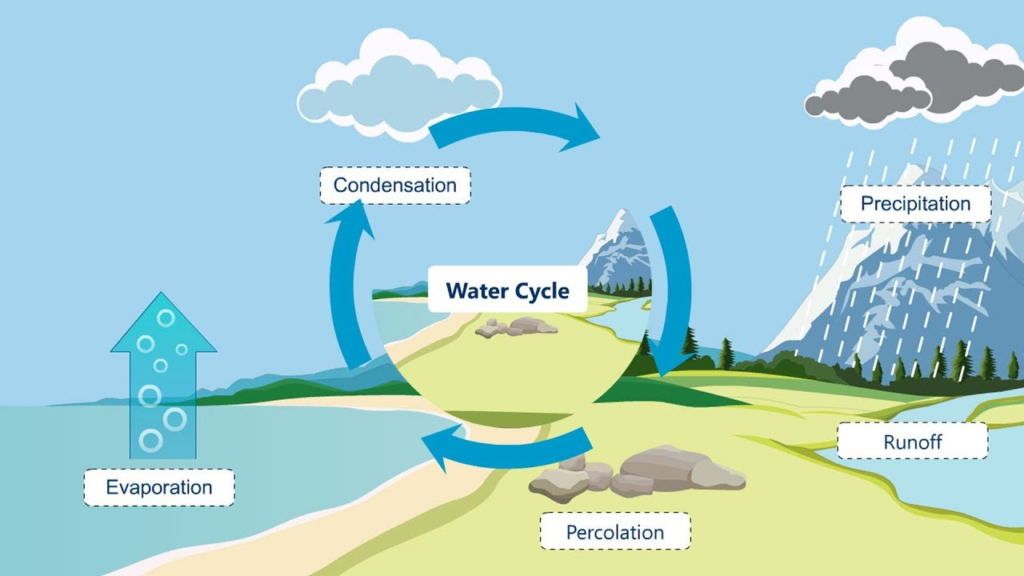
- Evaporation: Water from oceans, rivers, and lakes turns into water vapor due to the heat from the sun.
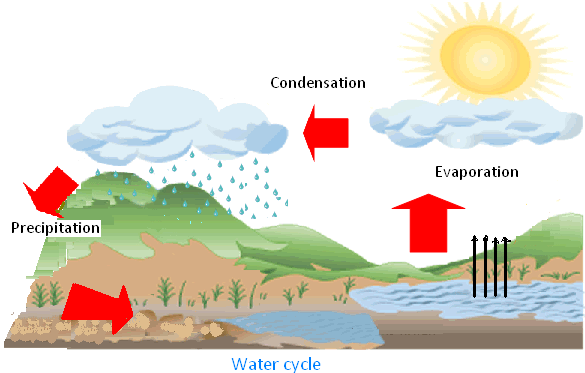
- Condensation: Water vapor in the air cools down and forms tiny droplets, making clouds.
- Precipitation: When clouds become heavy, water falls back to Earth as rain, snow, or hail.
- Collection: Water collects in rivers, lakes, oceans, or underground, completing the cycle.
Importance of the Sun:
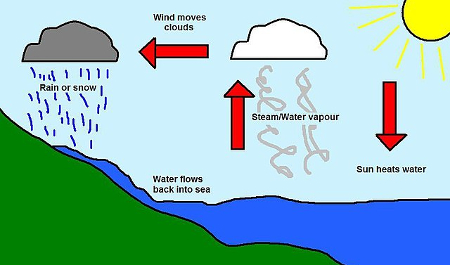
- The sun provides the energy needed for evaporation to start the water cycle.
Forms of Water in the Cycle:
- Liquid (water in rivers, lakes, oceans),
- Gas (water vapor during evaporation),
- Solid (ice or snow during freezing conditions).
Why is the Water Cycle Important?
- It provides fresh water for drinking, irrigation, and supporting life.
- It helps maintain the Earth’s temperature by redistributing heat.
Fun Fact:
- The water you drink today might have been part of a river, an ocean, or even a dinosaur’s drink millions of years ago!
Let’s practice!

