Forms Of Water

Key Notes:
Introduction to Water:
- Water is essential for all living things.
- It is found in different forms on Earth.
Three Forms of Water:
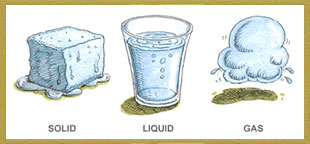
- Solid: Ice and snow are solid forms of water. Water freezes and becomes solid when the temperature is very cold (below 0°C or 32°F).
- Liquid: Water in rivers, lakes, and oceans is in liquid form. It is the most common form of water we use every day for drinking, cooking, and bathing.
- Gas: Water vapor is the gaseous form of water. It is invisible and formed when water is heated and evaporates.
How Water Changes Forms:
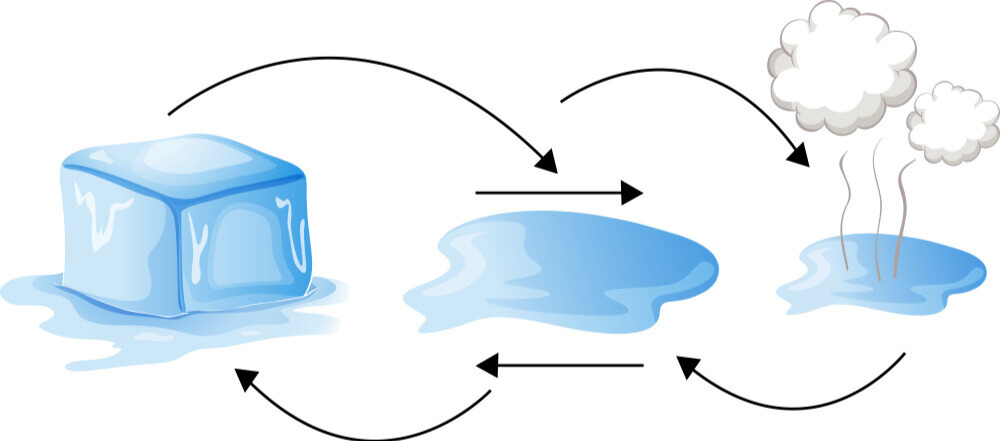
- Freezing: When water becomes very cold, it turns into ice (liquid to solid).
- Melting: When ice is heated, it changes back to water (solid to liquid).
- Evaporation: When water is heated, it turns into water vapor (liquid to gas).
- Condensation: When water vapor cools, it turns back into liquid water (gas to liquid).
Examples in Nature:
- Icebergs and glaciers represent water in solid form.
- Rivers, ponds, and rain are examples of liquid water.
- Clouds form when water vapor condenses, showing the gaseous form of water.
Water Cycle:
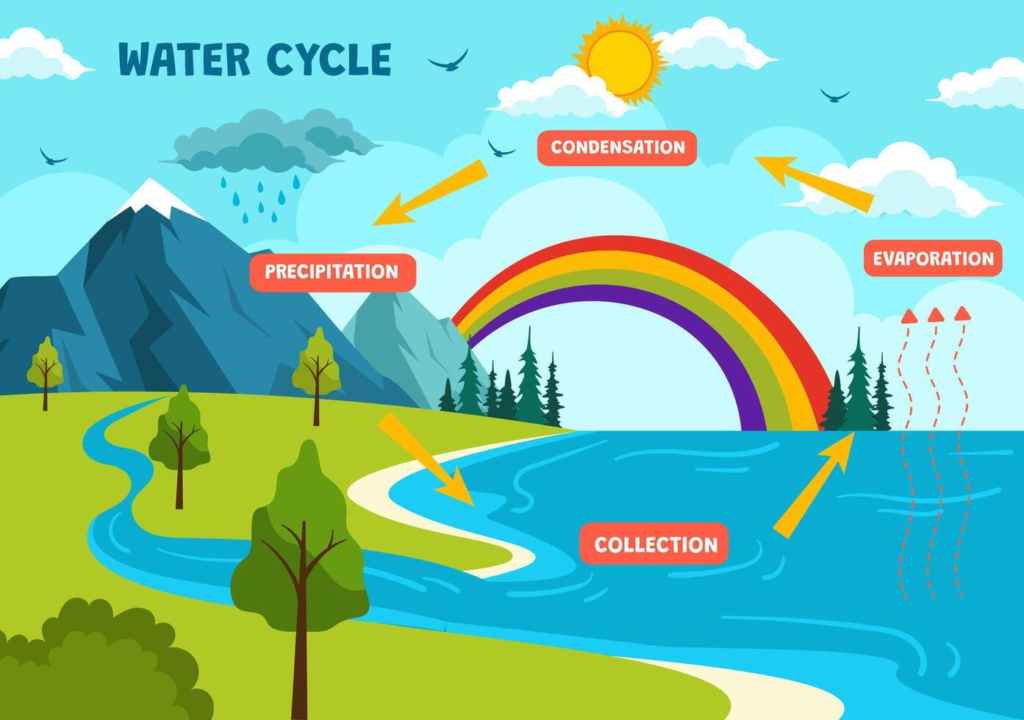
Water changes forms as part of the water cycle:
- Evaporation → Condensation → Precipitation → Collection.
This cycle helps distribute water across the Earth.
Importance of Water Forms:
- Solid water (ice) helps cool things and stores water in glaciers.
- Liquid water is vital for drinking, farming, and transportation.
- Water vapor is essential for forming clouds and precipitation.
Fun Facts:
- Nearly 70% of Earth’s surface is covered with water.
- Ice is less dense than water, which is why it floats.
Let’s practice!

