Living Things Produce Young Ones
key notes:
Definition of Reproduction:
Reproduction is the process by which living things make more of their own kind. This is how life continues from one generation to the next.
Types of Reproduction:
There are two main types of reproduction:
- Asexual Reproduction: One parent makes a copy of itself (e.g., plants growing from seeds).
- Sexual Reproduction: Two parents (a male and a female) produce offspring (e.g., animals like humans, dogs, and birds).
Animals:
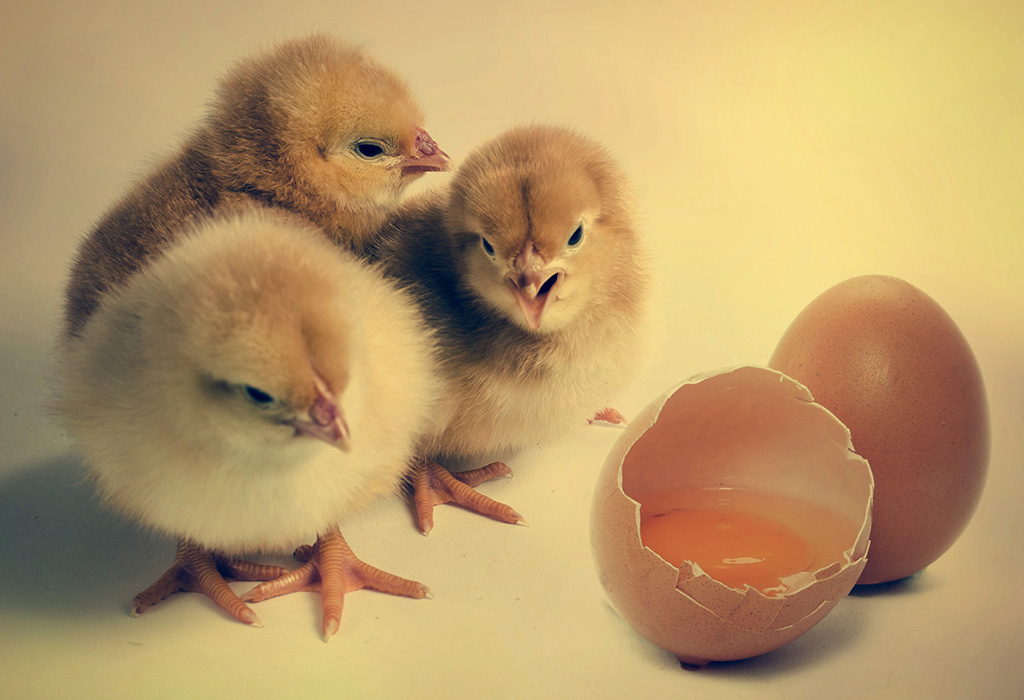

- Animals give birth to live young or lay eggs that hatch into young animals (e.g., dogs give birth to puppies, chickens lay eggs that hatch into chicks).
- Different animals have different ways of caring for their young (e.g., some animals protect their young after birth, while others leave them to grow on their own).
Plants:
- Plants reproduce by making seeds that can grow into new plants. Some plants also reproduce by spreading parts like roots or stems.
- Examples: Apple trees make seeds inside apples, and flowers make seeds that can grow into new flowers.
Growth and Development:
- Young ones grow and change into adults. For example, a caterpillar changes into a butterfly, and a tadpole becomes a frog.
Importance of Reproduction:
Reproduction helps to ensure that species survive and continue to exist on Earth.
Examples in Nature:
- Mammals like humans, dogs, and elephants give birth to live young.
- Birds, like chickens and ducks, lay eggs that hatch into young.
- Reptiles like turtles and snakes also lay eggs.
Let’s practice!

