Read clocks and write times
Key Notes :
Types of Clocks
- Analog clocks: Have numbers 1–12 and moving hands.
- Digital clocks: Show time using numbers only (e.g., 03:45).
Parts of an Analog Clock
- Hour hand: Short hand; shows the hour.
- Minute hand: Long hand; shows the minutes.
- (Optional) Second hand: Moves quickly and shows seconds.
Understanding Hours and Minutes
- A clock has 12 hours marked.
- The minute hand moves around the clock in 60 minutes.
- Each number on the clock represents 5 minutes.
Reading Time to the Hour
- When the minute hand is on 12, it’s an o’clock time.
- Example: If the hour hand is on 3 → it’s 3 o’clock (3:00).
Reading Time to the Half Hour
- When the minute hand is on 6 → it’s half past the hour.
- Example: Hour hand between 4 and 5, minute hand on 6 → 4:30.
Quarter Past and Quarter To (Optional/Advanced)
- Minute hand on 3 → Quarter past the hour (15 minutes).
- Minute hand on 9 → Quarter to the next hour (45 minutes).
- Example: 6:15 → Quarter past 6, 7:45 → Quarter to 8.
Writing Time
- Use the digital format: HH:MM (e.g., 2:00, 2:30, 3:45).
- Add a.m. (morning) or p.m. (afternoon/evening) if needed.
Practice with Real Clocks
- Practice setting and reading both analog and digital clocks.
Learn with an example
📗 What time does the clock show?
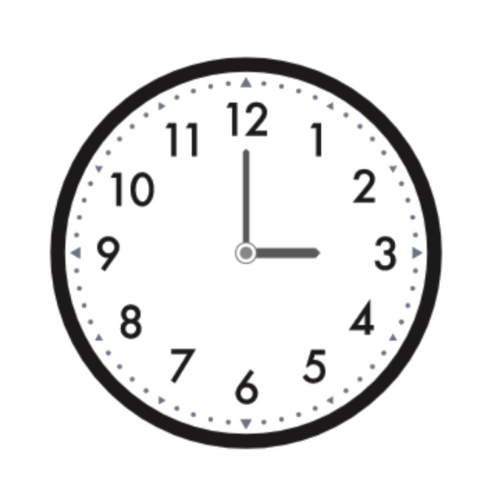

_______ : 00
- To find the hour, look at the hour hand.
- The hour hand is the shorter hand. It points directly to the 3.

- The hour hand shows 3 hours.
- The clock shows 3:00.
📗 What time does the clock show?
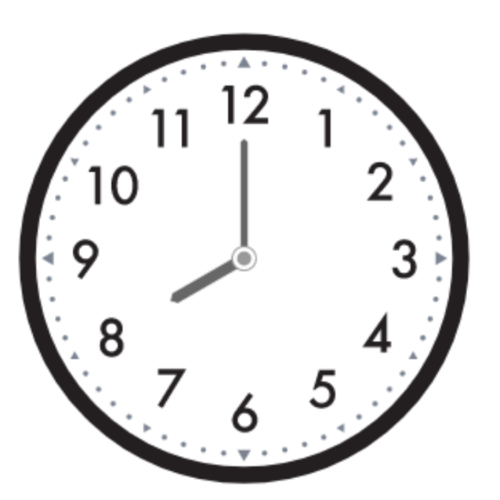

_______ : 00
- To find the hour, look at the hour hand.
- The hour hand is the shorter hand. It points directly to the 8.

- The hour hand shows 8 hours.
- The clock shows 8:00.
What time does the clock show?
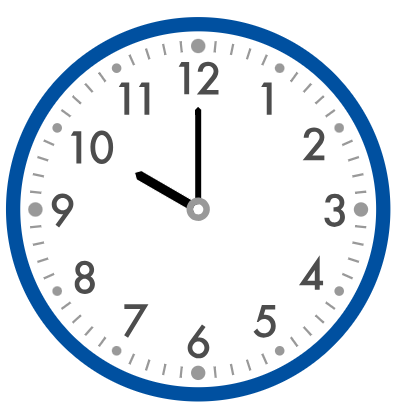
_______ : 00
To find the hour, look at the hour hand.
The hour hand is the shorter hand. It points directly to the 10.
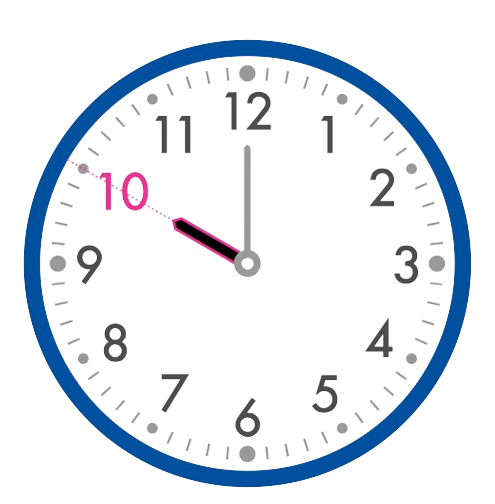
The hour hand shows 10 hours.
The clock shows 10:00.
Let’s practice!🖊️

